List of endocrine glands and their hormones and functions ppt – Commencing with “List of Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones and Functions,” this presentation delves into the intricacies of the endocrine system, illuminating its pivotal role in regulating myriad bodily functions. Hormones, the chemical messengers of our bodies, orchestrate a symphony of physiological processes, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Prepare to embark on an exploration of the major endocrine glands, their specialized hormones, and the diverse functions they govern. From the pituitary’s maestro-like control to the thyroid’s metabolic regulation, each gland plays a unique and indispensable role in maintaining homeostasis.
Introduction
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress response.
Hormones exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on target cells. Once bound, they initiate a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately lead to the desired physiological response.
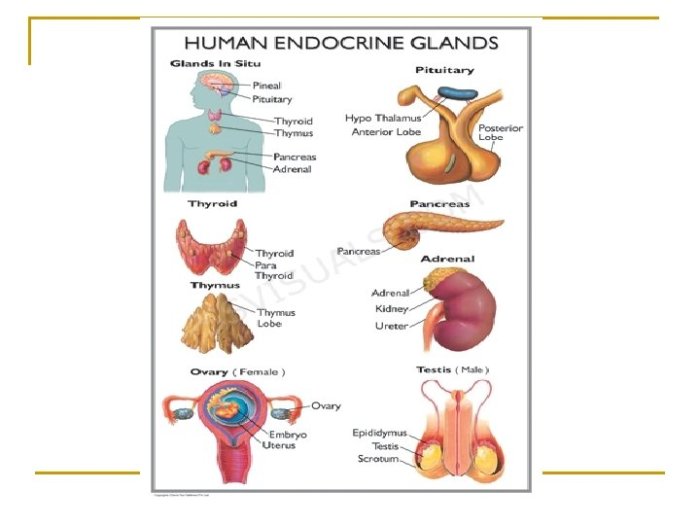
List of Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones: List Of Endocrine Glands And Their Hormones And Functions Ppt

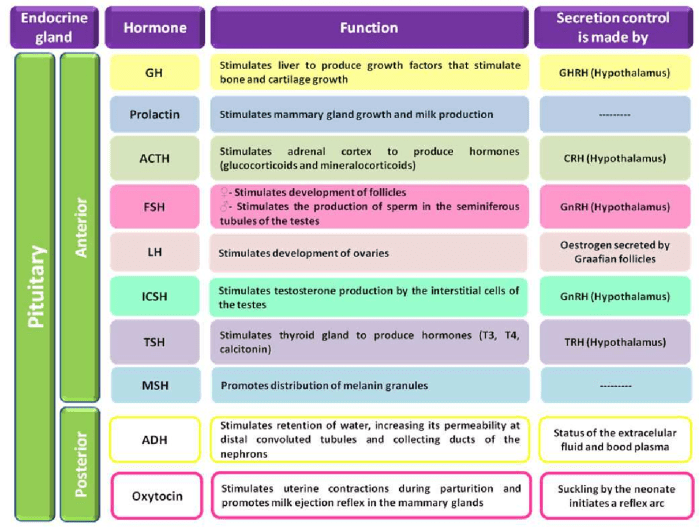
| Gland | Hormone | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pituitary | Growth hormone (GH) | Stimulates growth and development | Base of the brain |
| Pituitary | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Stimulates thyroid hormone production | Base of the brain |
| Pituitary | Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Stimulates adrenal hormone production | Base of the brain |
| Pituitary | Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Stimulates follicle development in ovaries and sperm production in testes | Base of the brain |
| Pituitary | Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Triggers ovulation in ovaries and testosterone production in testes | Base of the brain |
| Thyroid | Thyroid hormone (T3, T4) | Regulates metabolism, growth, and development | Neck |
| Parathyroid | Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Regulates calcium levels in the blood | Neck |
| Adrenal | Cortisol | Regulates stress response, metabolism, and blood pressure | Above the kidneys |
| Adrenal | Epinephrine (adrenaline) | Stimulates “fight or flight” response | Above the kidneys |
| Pancreas | Insulin | Lowers blood sugar levels | Behind the stomach |
| Pancreas | Glucagon | Raises blood sugar levels | Behind the stomach |
| Ovaries | Estrogen | Regulates female reproductive cycle and sexual characteristics | Pelvic cavity |
| Ovaries | Progesterone | Prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains pregnancy | Pelvic cavity |
| Testes | Testosterone | Regulates male reproductive cycle and sexual characteristics | Scrotum |
Elaborate on Hormone Functions
Growth Hormone (GH)
GH stimulates growth and development by promoting protein synthesis and cell proliferation. It also plays a role in metabolism and body composition.
Thyroid Hormone (T3, T4), List of endocrine glands and their hormones and functions ppt
Thyroid hormone regulates metabolism, growth, and development. It also affects heart rate, body temperature, and mood.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
PTH regulates calcium levels in the blood by increasing calcium absorption from the intestines and bones.
Cortisol
Cortisol regulates stress response by increasing blood sugar levels, suppressing inflammation, and boosting energy levels.
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Epinephrine stimulates the “fight or flight” response by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate.
Insulin
Insulin lowers blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake into cells.
Glucagon
Glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose from the liver.
Estrogen
Estrogen regulates the female reproductive cycle, develops secondary sexual characteristics, and protects against osteoporosis.
Progesterone
Progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains pregnancy by inhibiting uterine contractions.
Testosterone
Testosterone regulates the male reproductive cycle, develops secondary sexual characteristics, and increases muscle mass.
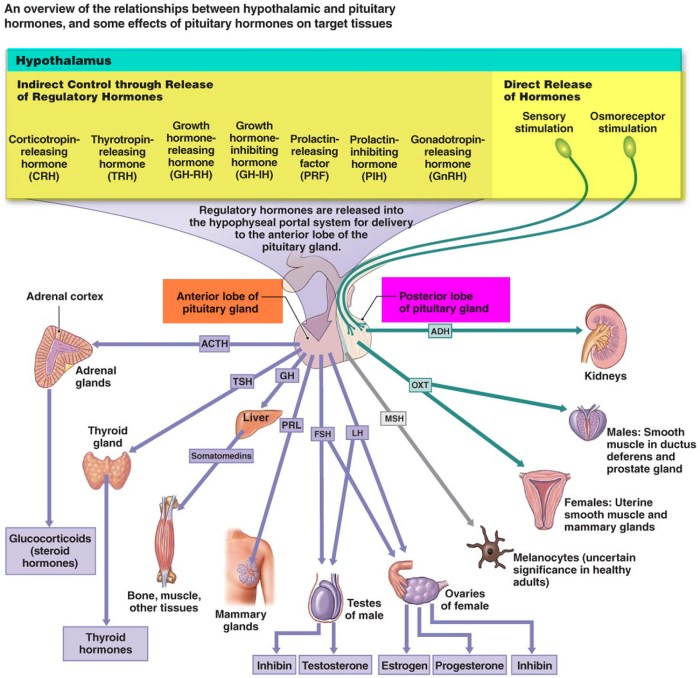
Regulation of Hormone Secretion
Hormone secretion is regulated by feedback loops involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and target glands.
In a negative feedback loop, the target hormone inhibits the secretion of the releasing hormone from the hypothalamus and the stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland.
In a positive feedback loop, the target hormone stimulates the secretion of the releasing hormone from the hypothalamus and the stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland.
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for overall health. Imbalances can lead to various endocrine disorders.
Clinical Significance
Hormonal imbalances can lead to endocrine disorders, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and growth hormone deficiencies.
Diabetes is a disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin deficiency or resistance.
Thyroid disorders include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Growth hormone deficiencies can result in stunted growth and developmental delays.
Treatment of endocrine disorders typically involves hormone replacement therapy or medications to regulate hormone secretion.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is responsible for regulating and coordinating various bodily functions through the secretion of hormones.
How do hormones exert their effects on target cells?
Hormones bind to specific receptors on target cells, triggering intracellular signaling cascades that elicit specific responses.
What is the role of the pituitary gland in hormone regulation?
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” secretes hormones that regulate the activity of other endocrine glands.